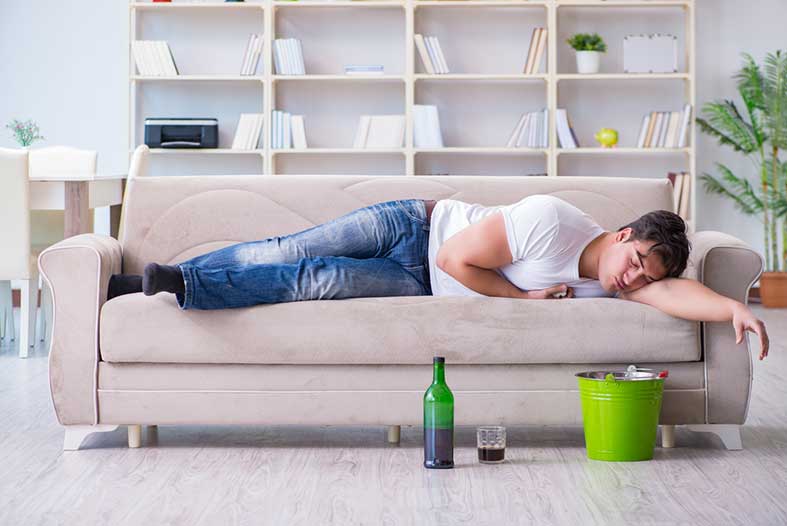
No party or holiday seems to be complete without alcohol! Whether it's to celebrate your favourite team winning a match or celebrate graduation. Alcohol is a widely ingested psychoactive substance and has been a component of human civilisation for centuries. Regular consumption of alcohol can have short-term as well as long-term effects on the body. Although moderate alcohol consumption can have some health benefits, excessive use can lead to numerous health problems, including liver disease, cancer, and mental health disorders.
The short-term effects of alcohol consumption can be seen immediately after consuming it. The initial consequences of alcohol consumption are feelings of relaxation, reduced inhibitions, and a sense of euphoria. However, as more alcohol is consumed, it can impair judgment, coordination, and memory. It can also cause blackouts when the person cannot recall events that occurred while under the influence of alcohol. Alcohol can also affect the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for motor coordination and balance, leading to impaired motor skills, difficulty walking and slurred speech. In addition, alcohol can hurt the digestive system, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. It can also raise heart rate and blood pressure, leading to an irregular heartbeat, chest pain, and even a heart attack. Alcohol can also cause severe dehydration, leading to headaches and fatigue.
The long-term effects of alcohol consumption can be more severe and potentially life-threatening. Excessive alcohol use can lead to numerous health problems, including liver disease, cancer, and mental health disorders. Long-term alcohol use can lead to liver cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, and liver cancer.
Alcohol can also harm mental health. Extreme alcohol use can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. It can also lead to memory loss and cognitive impairment, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks. In addition, alcohol increases the risk of developing certain kinds of cancer, such as breast and colon cancer. It also depletes the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections and diseases.
It is crucial to note that the consequences of alcohol can vary depending on a person's age, gender, weight, and overall health. It is recommended that individuals consume alcohol in moderation and seek medical help if they experience any adverse effects from alcohol use.
ALCOHOL’S PHYSICAL EFFECTS ON THE BODY
In this section, we will break down the effects of alcohol on the different organ systems of our body.
- CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Alcohol depresses the central nervous system, abbreviated as CNS. When alcohol is consumed, it crosses the blood-brain barrier and affects the brain's chemistry. The effects of alcohol on the CNS can be immediate and vary depending on the amount of alcohol consumed, the individual's body weight, and overall health.
The CNS controls most bodily functions, including movement, sensation, thought processes, and emotions. Alcohol consumption can have various effects on these functions. At low levels of alcohol consumption, the results are typically mild, such as increased relaxation and reduced inhibitions. However, as alcohol consumption increases, so do the effects on the CNS.
Alcohol can impact the brain's neurotransmitters, the chemicals that transmit signals throughout the brain. The neurotransmitter that is most affected by alcohol is gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is responsible for reducing activity in the brain and producing a calming effect. Alcohol increases the activity of GABA, which is why it can create feelings of relaxation and sedation.
However, alcohol can also decrease the activity of another neurotransmitter, glutamate. Glutamate is responsible for stimulating brain activity, and a decrease in its activity can cause a reduction in cognitive function, such as memory and concentration. This is why individuals who have consumed excessive amounts of alcohol may experience blackouts or memory loss.
Alcohol can also affect the brain's reward system by increasing the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that produces feelings of pleasure and reward. This is why alcohol can be addictive, as individuals may seek the pleasurable effects of alcohol consumption.
Long-term alcohol consumption can have severe effects on the CNS. It can lead to the development of brain damage and neurological disorders, such as dementia, epilepsy, and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. These conditions are caused by alcohol's impact on the brain's structure and function and its effect on neurotransmitters and other chemicals in the brain.
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Alcohol consumption can also have a significant impact on the digestive system. When alcohol is ingested, it enters the gut and small intestine, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. The liver then metabolises the alcohol and breaks it down into substances that can be eliminated from the body. However, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to several unfavourable effects on the digestive system.
Alcohol also irritates the lining of the stomach, leading to inflammation and digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. It can also cause the stomach to produce more acid, which can lead to heartburn and stomach ulcers. Long-term alcohol consumption can lead to inflammation and scarring of the liver, known as cirrhosis. This can lead to various symptoms, such as fatigue, abdominal pain, and yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to pancreatitis, a condition where the pancreas becomes inflamed. This can cause symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Chronic alcohol use can lead to an increased risk of developing pancreatitis, which can lead to long-term damage and complications.
In addition, alcohol can interfere with the absorption of essential nutrients such as vitamins and minerals, leading to malnutrition and associated health problems. This is because alcohol can damage the cells lining the intestines, reducing their ability to absorb nutrients properly.
- IMMUNE SYSTEM
Alcohol consumption can also significantly impact the immune system, which is responsible for resisting infections and diseases. Alcohol can repress the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to defend itself against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
One of the ways alcohol affects the immune system is by reducing the production of cytokines, which are proteins that play an essential role in the body's immune response. Cytokines are responsible for signalling the immune system to produce antibodies and fight off infections. When alcohol is consumed, the production of cytokines is diminished, making it more difficult for the body to mount an effective immune response.
White blood cells are essential to fight pathogens. In addition, alcohol can also interrupt the production of white blood cells. This can make it difficult for the body to identify and eliminate harmful pathogens, leaving individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Long-term alcohol consumption can also lead to chronic inflammation, which can contribute to a variety of health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Chronic inflammation weakens the immune system and makes it difficult for the body to battle infections and illnesses.
- EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON THE HEART
Alcohol consumption has a substantial impact on the heart and blood vessels. While moderate alcohol consumption has been associated with a lower risk of heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption leads to several negative outcomes.
One of the most immediate effects of alcohol on the heart is an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This can put additional strain on the heart and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Long-term alcohol consumption can also lead to the development of high blood pressure, which is a prominent risk factor for heart disease.
Excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to an enlarged heart, a condition known as cardiomyopathy. Symptoms of cardiomyopathy may present as fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and ankles. In severe cases, cardiomyopathy may progress to heart failure and even death.
Alcohol consumption also increases the risk of arrhythmias, which are abnormal heart rhythms that can lead to palpitations, dizziness, and fainting. Long-term alcohol consumption can also lead to the development of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON THE TEETH AND ORAL CAVITY
Alcohol consumption can also have negative effects on the oral cavity. One of the most immediate effects of alcohol consumption is dry mouth, which occurs when the body does not produce enough saliva. Saliva is essential for maintaining oral health, as it helps to neutralise acids in the mouth and wash away food debris and bacteria that can lead to cavities and gum disease.
Alcohol can also irritate the tissues in the mouth, leading to inflammation and soreness. This can make it more difficult to chew and swallow food and lead to the development of sores and ulcers in the mouth.
Another damaging effect of alcohol consumption on oral health is the increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease. Alcohol can erode tooth enamel, making teeth more susceptible to decay. It also causes inflammation and infection of the gums, leading to gum disease and tooth loss.
In addition, alcohol consumption can increase the risk of oral cancer. This is because alcohol is a carcinogen, which can damage DNA and increase the risk of cancerous cell growth. When combined with other risk factors, such as smoking or tobacco use, the risk of oral cancer increases significantly.
Finally, alcohol consumption can also contribute to bad breath. This is because alcohol can lead to a dry mouth, which can cause the buildup of bacteria that produce odour.
- EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Alcohol consumption negatively affects sexual and reproductive health. In the short term, alcohol can impair sexual function by decreasing libido, delaying orgasm, and causing erectile dysfunction in men. In women, alcohol consumption can lead to vaginal dryness and reduced sexual arousal.
Long-term alcohol consumption can also lead to a variety of negative effects on reproductive health. For men, high levels of alcohol consumption can lead to a decrease in testosterone levels, which can result in reduced sperm production and fertility. It can also lead to the development of testicular atrophy, which is the shrinking of the testicles.
In women, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and an increased risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. It can also increase the risk of breast cancer.
Overall, excessive alcohol consumption can have negative effects on sexual and reproductive health, including impaired sexual function, decreased fertility, and an increased risk of breast cancer, miscarriage, and stillbirth. It is essential to consume alcohol in restraint and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support sexual and reproductive health.
- EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON GROWTH AND MUSCLES
Excessive alcohol consumption can also have unfavourable effects on growth and muscles. Alcohol can meddle with the production of growth hormone, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. It can also impair protein synthesis, vital for building and maintaining muscle mass. In addition, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to dehydration, which can cause muscle cramps and weakness. Long-term alcohol consumption can also lead to the development of muscle wasting and weakness, which can significantly impact overall health and well-being. It is essential to consume alcohol in moderation and maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine to support muscle growth and overall health.
- EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON GLUCOSE LEVELS OF THE BODY
Alcohol consumption can have a consequential impact on glucose levels in the body. In the short term, alcohol can cause a drop in blood glucose levels, leading to symptoms such as tremors, confusion, and dizziness. This is because alcohol can interfere with the liver's ability to produce glucose, which is an essential source of energy for the body.
In the long term, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to the development of insulin resistance, which is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less responsive to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood glucose levels. This can lead to an increase in blood glucose levels, which can cause damage to the blood vessels and nerves over time.
Alcohol consumption can also contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, which can further exacerbate insulin resistance and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. In addition, alcohol consumption can lead to weight gain, which is another risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Overall, excessive alcohol consumption can have adverse effects on glucose levels in the body, including a drop in blood glucose levels in the short term and the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in the long run. It is essential to consume alcohol in moderation and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support glucose regulation and overall health.
We hope this blog provided you with some beneficial insights into the effects of alcohol on the body. Anything done in moderation is fine and may yield good results, as we have already seen. However, uninhibited consumption of alcohol should be avoided at all costs. If you liked this blog and wish to access more such content, please visit Cure Direct Hub Website and channel. Cure Direct Hub connects you with healthcare providers around the world. We aim to facilitate the best healthcare at affordable prices overseas. For more information, please reach out to us. Our team of compassionate and excellent professionals is here to assist you and your family in your journey to exceptional health.

Written By Dr. Jigisha Chhangani
currently pursuing her specialization in Maxillofacial Surgery. She is a research fellow in minimally invasive surgery. Her passion for writing extends beyond academics. She is an active, creative writer for dental and medical blogs, articles, and ghost-written books. She is enthusiastic about preventive dental care and has worked avidly in public and dental health during her tenure as a consultant at a trust-operated dental clinic and hospital. She aims to educate the masses and instill good practices about oral and overall health.
View ProfileWatch YouTube video related to Article
Products related to treatment
Similar Articles
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT FUE HAIR TRANSPLANT
- Feb 19, 2024
Hair transplant has gained immense importance in the present times. Cure Direct Hub has made it possible for people to get premium hair transplant service...

WHAT DOES ALCOHOL DO TO YOUR BODY?
- Feb 20, 2024
No party or holiday seems to be complete without alcohol! Whether it's to celebrate your favourite team winning a match or celebrate graduation. Alcohol is a widely ingested psychoactive substance and has been a component of human civilisation for centuries. Regular consumption of alcohol can have short-term as well as long-term effects on the body. Although moderate alcohol consumption can have some health benefits, excessive use can lead to numerous health problems, including liver disease, cancer, and mental health disorders.

 Arabic
Arabic Spanish
Spanish Hindi
Hindi Tamil
Tamil Thai
Thai Swedish
Swedish Arabic
Arabic Spanish
Spanish Hindi
Hindi Tamil
Tamil Thai
Thai Swedish
Swedish



